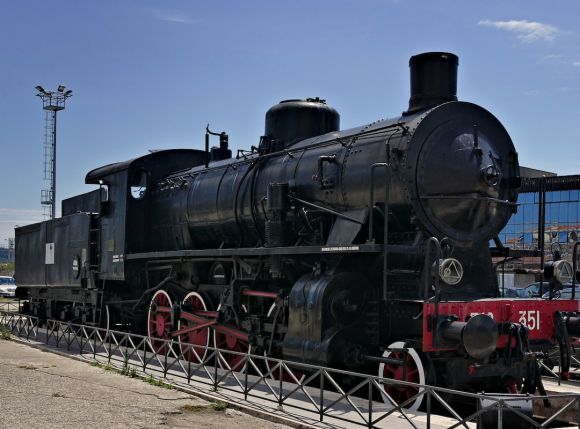
The steam locomotive era was a time of great innovation and progress in the world of railroads. During this period, steam locomotives were the primary mode of transportation, revolutionizing the way people and goods were transported across vast distances. One of the key aspects of these locomotives was their ability to generate and utilize heat, which played a crucial role in their operation. In this article, we will explore the significance of heat in the steam locomotive era.
The Birth of Steam Locomotives
Before delving into the role of heat in steam locomotives, it is important to understand how these machines came into existence. The steam locomotive was first developed in the early 19th century, marking a significant milestone in the history of transportation. It was powered by steam, generated by burning coal or wood, which in turn propelled the locomotive forward. This process relied heavily on the production and management of heat.
The Firebox: The Heart of the Locomotive
At the core of every steam locomotive was the firebox, a designated area where fuel was burned to produce heat. This heat was then transferred to water in the boiler, creating steam. The firebox was meticulously designed to maximize heat production while ensuring the safety of the locomotive and its crew. The type and quality of fuel used, along with the skill of the fireman, played a crucial role in maintaining the optimal heat levels within the firebox.
The Boiler: Harnessing the Power of Steam
Once the heat was generated in the firebox, it was transferred to the boiler, where water was heated to its boiling point, creating steam. The boiler was a robust and complex structure, capable of withstanding high-pressure steam. It was essential in converting the heat energy from the firebox into mechanical energy, which propelled the locomotive’s wheels. The efficient utilization of heat within the boiler was crucial for the locomotive’s overall performance and speed.
Regulating Heat: The Role of the Fireman
The fireman, a key member of the locomotive crew, played a vital role in regulating the heat within the locomotive. It was their responsibility to ensure a steady supply of fuel to the firebox, maintaining the optimum temperature for efficient steam production. The fireman had to carefully monitor the firebox, adjusting the fuel and air supply to achieve the desired heat levels. Their skill and experience were essential in preventing overheating or underutilization of heat in the locomotive.
The Impact of Heat on Efficiency and Performance
The efficient utilization of heat was crucial for the locomotive’s efficiency and performance. A well-maintained firebox and boiler, along with skilled firemen, ensured that the locomotive could generate sufficient steam to power its wheels. This, in turn, allowed the locomotive to achieve higher speeds and carry heavier loads. Heat management was not only essential for the locomotive’s operation but also for the safety of its crew and passengers.
The Legacy of the Steam Locomotive Era
The steam locomotive era had a profound impact on the world of transportation. It paved the way for the development of more advanced locomotive technologies and transformed the way people and goods were transported. While steam locomotives have largely been replaced by electric and diesel locomotives, their legacy lives on. The efficient utilization of heat in the steam locomotive era set the foundation for future innovations and advancements in the field of rail transport.
In conclusion, the steam locomotive era was characterized by the significant role that heat played in the operation of these machines. From the firebox to the boiler, every aspect of the locomotive relied on the efficient generation and utilization of heat. Skilled firemen played a crucial role in regulating heat levels, ensuring the locomotive’s performance and safety. The legacy of the steam locomotive era, with its emphasis on heat management, continues to influence the world of rail transport to this day.